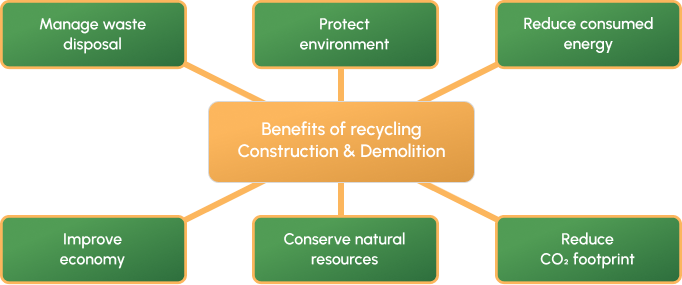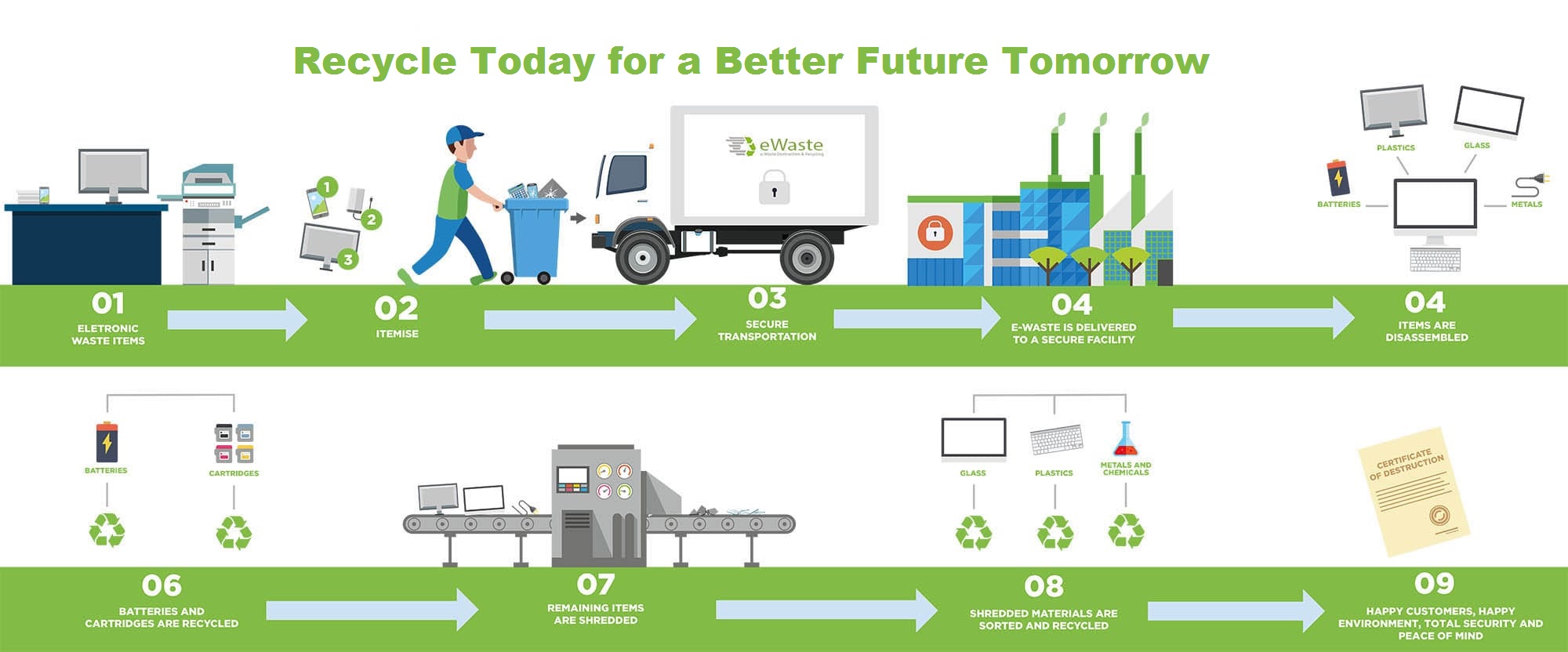
Waste Collection
Expert team equipped with latest facilities engaged in regular collection of waste from residential and commercial sources
Segregation
Skilled staff ensures proper segregation into recyclable categories of waste for effective processing.
Processing
Adequate infrastructure with State-of the- art technologies and trained workforce guarantee effectual recycling process of global standards in tandem with all rules of the land.

Recycling
Scientific processing, advanced methodology and incessant monitoring ensure superior recycling.

Disposal
We ensure that all residue materials are scientifically disposed as mandated by regulatory agencies of the land.